
India Gets A National Logistics Policy
Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi launched the National Logistics Policy (NLP) at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi on 17th September 2022. NLP is a...
What is the e-way bill and why is it important? What are the other benefits of the e-way bill system?

After rolling out GST last year, Government of India introduced the e-way bill system in February 2018. While the initial endeavour to roll out the new tax collection method was not successful, it fared much better in the second attempt made in April 2018. By end of May 2018, the GST e-way bill system had been successfully implemented for inter-state movement of goods in 21 states and six Union Territories.
After effective execution of the new process in interstate goods movement, starting June 2018, GST e-way bill rule has been implemented for intra-state movement of goods throughout the country.
Why is the GST e-way bill so important?
The e-way bill system is a part of the GST regime. This system has been created with the aim to systematize logistical movement of goods in the country, improve and increase tax collection, and in turn control tax evasion.
What is an e-way bill?
The GST e-way bill is an electronic document that is required to be carried by the transporter when transporting goods worth more than INR 50,000 via a single bill/delivery challan/invoice.
What are the other benefits of the e-way bill system?
Apart from making the country’s tax structure efficient, it is also believed that GST e-way bill system will provide the following benefits to the trade:
When should an e-way bill be generated or issued?
An e-way bill is required to be generated or issued when a consignment worth INR 50,000 is going to be transported via a single delivery challan/invoice/bill. This value can be the total of all goods transported in the vehicle or of the invoice of each shipment being transported in a vehicle. Such movement of goods can be due to reasons of supply of goods, return of goods, or purchase (inward supply) of goods.
A GST e-way bill also needs to be compulsorily generated in the following scenarios:
Are any goods exempt under the e-way bill generation rule?
The movement of the following goods does not require an e-way bill:
Who is required to generate an e-way bill?
A registered person (trader, seller, buyer, consignor, consignee, transporter) is required to generate an e-way bill.
An unregistered person also has to register on the e-way bill generation portal. However, an unregistered user is exempt from generating an e-way bill only if he is supplying goods to a registered person. In such a scenario, the registered person will be responsible for generating an e-way bill.
Is an e-way bill required in all movement of goods?
No, there are some exceptions where an e-way bill is not required. For example, an e-way bill is not required for:
From where and how to generate an e-way bill?
It’s simple! To generate an e-way bill all you need to do is register on the e-Way Bill System portal.
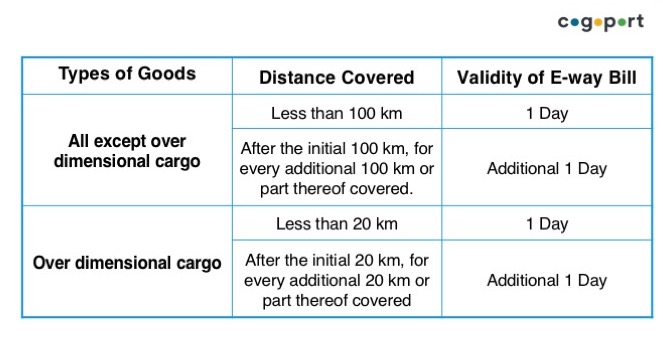
Does an e-way bill have a validity period? What is the validity period?
Yes, e-way bills have a validity period. It is based on the distance that the goods are transported. The validity period starts from the date and time of generation of an e-way bill.
What are the documents required for generating an e-way bill?
The following documents are required for generating an e-way bill:
For more information on the GST E-way Bill system, processes, and how to generate an E-way Bill visit Goods and Services Tax e-Way Bill System Portal.