Tariff Pause: How Indian Traders Can Take Advantage
The 2025 global tariff pause offers Indian exporters a rare opportunity to reduce duties on key exports like textiles, pharma, and machinery...
Know about Export Promotion Councils in India, its roles, functions, benefits, types, current trends and how to register with them.

Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) are organisations set up by the Government of India to help and assist Indian exporters by providing access to international markets, promoting Indian products through various activities and increasing the overall exports from India.
Every country has their own export promotion organisations to perform this job. In India, there are about 37 organisations that cater to exporters of different product categories. This categorisation provides better focus in promoting products and helps EPCs offer better assistance to exporters.
This blog attempts to equip exporters with all the relevant information on EPCs including:
Promoting exports is not new as countries worldwide have been doing this since time immemorial. It came to the limelight after the second world war when a structured approach was brought to the act of export promotion. In India, Federation of India Export Organisations, (FIEO) the apex body for export promotion was established in 1965 for this purpose.
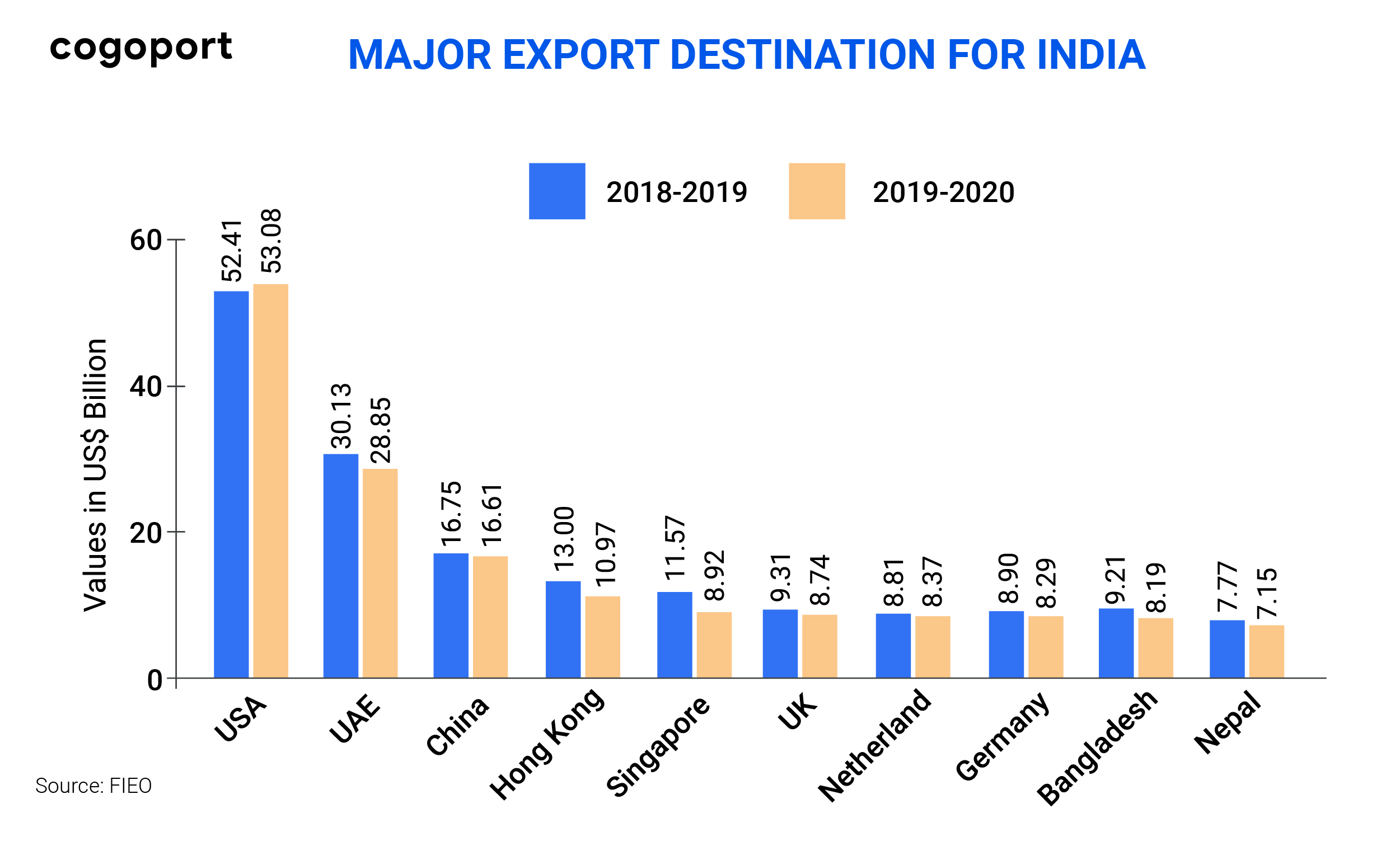

According to the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation (MoSPI) India was the 18th largest exporting nation in the world in 2019. But, the global share of the Indian exports was only 1.72% in that year. This meagre figure explains a lot as to why export promotion is needed for a country like India. Figures 1 and 2 clearly show that there is a lot of potential that exists for Indian exports in the international markets and India can increase its scope of exports through effective promotion. The role of export promotion councils come into picture here as they are established with the sole purpose to promote India as a quality supplier of products and services that are in demand in international markets.

In India, different export promotion councils (EPCs) are created to cater to the specific requirements of different export products. As every product category viz. electronic goods, apparel, food products, etc. have their own requirements and export-related challenges, the respective export promotion councils take on the responsibility to help exporters overcome challenges for those product categories and increase exports.
EPCs can be considered as a bridge between Government and exporters that coordinates with both the parties with the primary goal of boosting exports. The councils are formed as non-profit organizations under the Companies Act / Societies Registration Act. In addition to these councils, some export industries have Commodity Boards and Export Development Authorities.
Commodity Boards and Export Development Authorities were set up through special Acts passed in the Parliament.
FIEO is the apex body of all the export promotion councils. It acts as the crucial interface between Indian exporters, Central Government, State Governments, financial institutions, ports, railways, surface transport and other concerned stakeholders. It is estimated that FIEO serves more than 200,000 exporters from all the goods and services industries either directly or indirectly.
For simplicity, the word abbreviation ‘EPCs’ is used to collectively represent these organisations in this article. Further, all the above-mentioned organisations fall under the purview of the Ministry of Commerce.
Below is the comprehensive list of EPCs, Commodity Boards and Export Development Authorities:

The primary role and function of EPCs is to showcase India as the preferred destination for export of high-quality products and services. To achieve this, the EPCs represent India and its exporters in the international markets and promote the products through various means. While consolidating exports in current export destinations, EPCs are also required to help exporters in identifying new markets and expanding their export basket.
On the other hand, they also help the Government in framing effective trade policies by providing insights about the issues faced by exporters in international markets.
The EPCs are constituted as autonomous bodies with independent functioning and decision-making powers. Nevertheless, any laws and by-laws devised / modified by the Central Government from time to time, apply to all the EPCs and they are required to follow them.

Registering with an EPC has many benefits for the exporter. The registration and membership rules of EPCs are governed by the Foreign Trade Policy and EPCs’ Memorandum of Understanding and Articles of Association.
RCMC – key document
The Foreign Trade policy of the Government of India requires exporters to register with EPCs to get a Registration Cum Membership Certificate (RCMC). This is a key document for exporters as they cannot claim the benefits of incentive schemes announced in the Foreign Trade Policy without RCMC. Once issued, it is valid for 5 years.
RCMC issuing authorities
EPCs are authorized to issue RCMC. For instance, a leather exporter may apply for RCMC with the Council for Leather Exports; a pharmaceutical exporter must register with the Pharmaceutical Export Promotion Council and so on. This way the government has made it easier for exporters to register with their respective product/service promotion councils.
However, in case of multi-product exporters (who export two or more products each belonging to different industries and their main line of business is not settled) or if an export product is not covered under any of the export promotion councils, Government (for such cases) has authorized FIEO to issue RCMC. So, all multi-product exporters (who are yet to decide on their main line of business) or exporters whose products are not covered under any of the EPCs can apply for RCMC with the FIEO.
For multi-product exporters whose registered office or head office is located in the North Eastern States, RCMC can be obtained from Shellac & Forest Products Export Promotion Council (except for the products covered under APEDA, Spices Board and Tea Board).
To apply for RCMC from any of the EPCs, exporters must fill the application form that can be downloaded from respective websites of EPCs. Following documents must be submitted along with it:
OR
Furnish any further evidence for being manufacturer exporter by providing any of the documents being manufacturer exporter as per the undertaking on non-judicial stamp paper.
To apply for FIEO membership, the exporters must download and fill the application form and submit the following documents along with it:
The difference between EPCs and Commodity boards lie in the way they are set up and run. The table below provides more details on the same.

When it comes to the performance of EPCs in achieving their objectives, fingers are pointed at them questioning their effectiveness, especially in the backdrop of stagnating exports between 2014 and 2020.
One must, however, note that EPCs being non-profit organisations, have to raise funds to sustain themselves. Promotional activities are carried out through funds provided by the Government through various schemes like Market Development Assistance (MDA) or Marketing Access Initiative (MAI). Their funding primarily comes from the annual membership fees, EPCs as such cannot spend in a huge way in export promotion programmes. But that does not mean that they do not keep their members happy. The export community feels that EPCs are doing all they could in export promotion. There are other external issues (out of control of EPCs) that play a major part in export stagnation, including uncertainty in export markets, falling global demand, increased trade protectionism, lack of free trade agreements with major export partners, delays in releasing export benefits, inherent flaws in formulating trade policy etc.
Government on the other hand feels that it is prudent to review and restructure (and if necessary, close) certain EPCs based on their performance. For instance, the Ministry of Textiles in July/August 2020, abolished five advisory boards under its purview and in March 2021, another entity related to the same ministry, the Handicraft & Handlooms Export Corporation was shut down as it was consistently incurring losses since 2015-16.
Cogoport advises exporters / shippers to take a note on above mentioned points and keep abreast of latest information and happenings related to your EPCs. Check periodically with your respective EPCs on various parameters that directly or indirectly help in your exports.